Understanding Nursing Teaching on Hypertension, the role, responsibilities and Empowering Patients to Manage Their Health.
Hypertension, commonly known as high blood pressure, is a chronic condition that significantly increases the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other complications. For nurses, teaching patients about hypertension is not only a critical aspect of care but also an opportunity to empower individuals to take control of their health. Proper education on hypertension can lead to better management, improved patient outcomes, and a reduction in the burden of cardiovascular diseases globally.
Understanding Hypertension
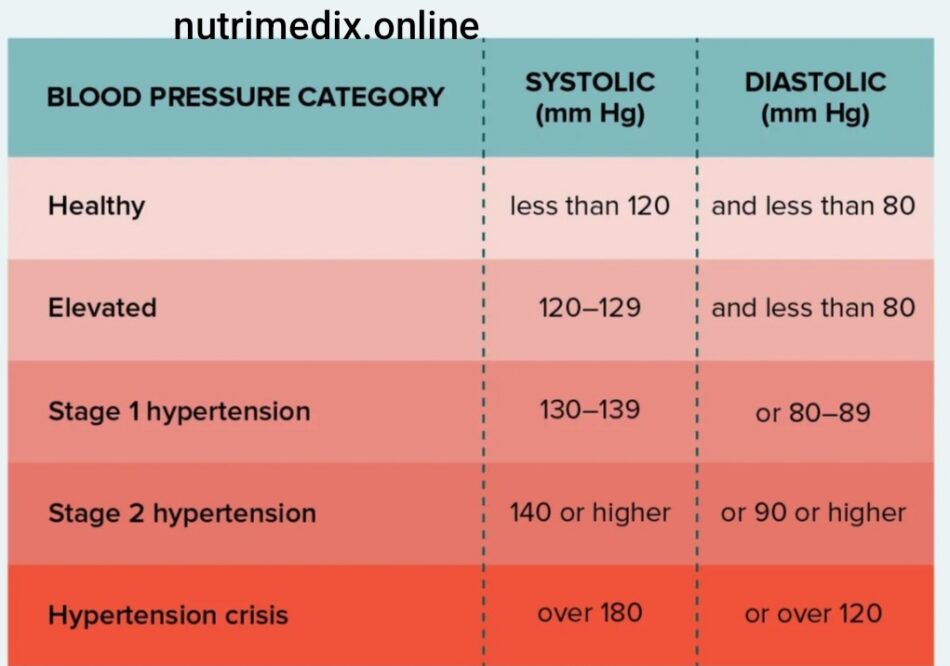
Hypertension occurs when the force of the blood against the walls of the arteries is consistently too high. It is often referred to as the “silent killer” because it typically has no symptoms until severe damage occurs in the heart, blood vessels, kidneys, or other organs. Nurses need to ensure that patients understand the two key measures of blood pressure:
- Systolic pressure (the top number): Measures the pressure in the arteries when the heart beats.
- Diastolic pressure (the bottom number): Measures the pressure in the arteries when the heart is at rest between beats.
The normal blood pressure range is usually less than 120/80 mmHg, while consistent readings above 140/90 mmHg are classified as hypertension.
Nursing Responsibilities in Hypertension Teaching:
- Assess Patient Knowledge: Evaluate the patient’s understanding of hypertension and identify learning barriers.
- Provide Clear Information: Explain hypertension, its effects, and the importance of controlling it in simple language.
- Teach Self-Monitoring: Instruct patients on how to measure blood pressure at home and recognize warning signs of hypertensive crises.
- Promote Medication Adherence: Educate patients about their medications, their importance, and encourage adherence.
- Offer Lifestyle Guidance: Provide advice on diet, exercise, and weight management to help control hypertension.
- Encourage Smoking Cessation & Alcohol Limitation: Educate on the risks of smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, and provide resources for quitting.
- Provide Emotional Support: Help patients cope with the stress of managing hypertension and offer mental health resources if needed.
- Coordinate Follow-Up Care: Ensure regular monitoring and ongoing education to keep patients on track.
- Advocate for Patient-Centered Care: Develop individualized care plans that fit the patient’s needs and preferences.
- Monitor for Complications: Watch for signs of hypertension-related complications and intervene early.
- These steps plays a key role in teaching nursing on Hypertension
- https://nutrimedix.online/hypertension-causes-symptoms-and-5-tips-to-cure
The Role of Nursing teaching on Hypertension Education
Nurses play a pivotal role in patient education about hypertension, focusing on prevention, lifestyle changes, and adherence to treatment plans. Effective education involves clear communication, patient-centered strategies, and ongoing support. Here are the key areas that nurses cover when teaching patients about hypertension:
- Risk Factors and Prevention
Nurses must educate patients about the risk factors for hypertension, which include:
- Unhealthy diet, particularly high in salt, fat, and cholesterol.
- Sedentary lifestyle and lack of physical activity.
- Obesity or being overweight.
- Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
- Stress and poor management of mental health. By helping patients understand modifiable risk factors, nurses can encourage preventive measures such as adopting a healthy diet, regular exercise, smoking cessation, and stress management techniques.
- Monitoring Blood Pressure
Teaching patients how to properly monitor their blood pressure at home is vital. Nurses should demonstrate how to use a home blood pressure monitor and interpret readings. They should emphasize:
- The importance of consistency (same time each day, relaxed state).
- Accurate recording of results to share with healthcare providers.
- Immediate action if readings are consistently high or low.
- Medication Adherence
Many patients with hypertension are prescribed medications such as diuretics, ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, or calcium channel blockers. Nurses should educate patients on:
- The importance of adhering to their medication regimen.
- Potential side effects and how to manage them.
- The dangers of skipping doses or discontinuing medication without consulting a healthcare provider.
- Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle changes are crucial for managing hypertension. Nurses can provide detailed advice on:
- Diet: Recommending the DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet, which emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low sodium.
- Exercise: Encouraging at least 30 minutes of moderate physical activity most days of the week.
- Weight Management: Assisting patients in setting realistic weight loss goals if they are overweight or obese.
- Alcohol and Smoking: Offering resources for smoking cessation programs and advising on limiting alcohol intake.
- Recognizing and Managing Hypertension Complications
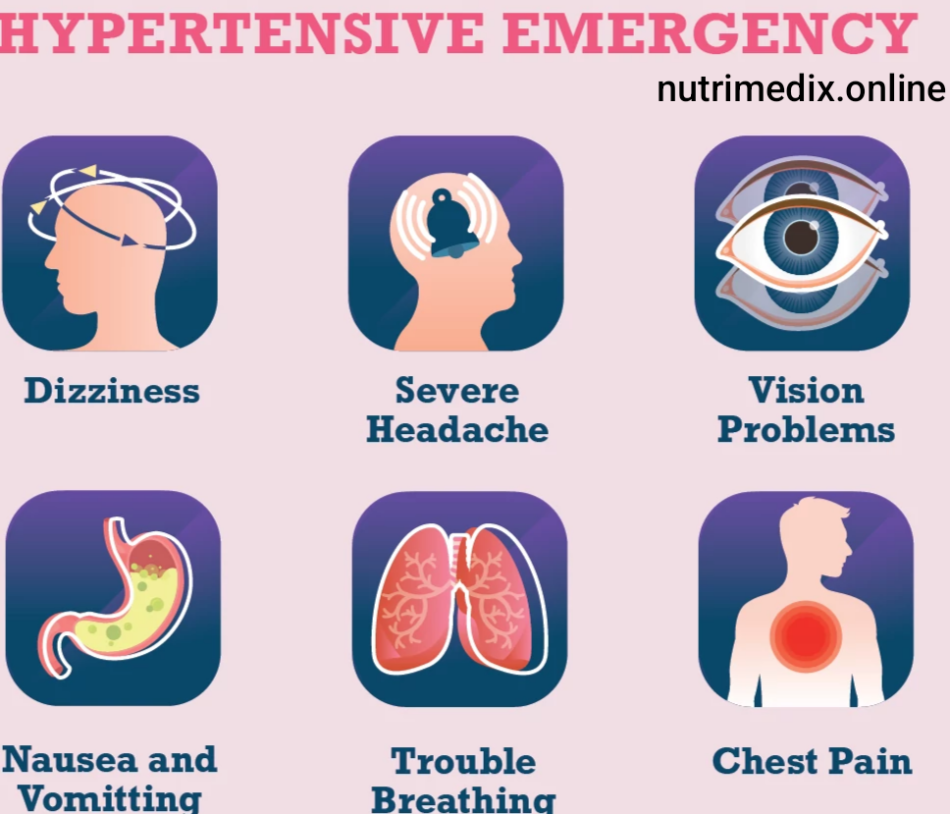
Nurses should teach patients about the potential complications of unmanaged hypertension, such as heart attack, stroke, kidney damage, and vision loss. They should also guide patients on the signs and symptoms of hypertensive crises, such as severe headaches, chest pain, or shortness of breath, and emphasize the importance of seeking emergency care in such cases. - Emotional and Psychological Support
Hypertension can be a source of anxiety for many patients. Nurses should provide emotional support, helping patients to cope with the stress of managing a chronic condition. This may include referrals to counseling services or support groups if needed.
Strategies for Effective nursing Hypertension Teaching
To ensure that patient education is successful, nurses should adopt a variety of strategies:
- Tailored Education: Customize the teaching based on the patient’s age, literacy level, cultural background, and personal health goals.
- Use of Visual Aids: Provide brochures, charts, or videos that visually explain blood pressure, risk factors, and lifestyle changes.
- Interactive Learning: Engage patients by asking questions, encouraging them to set personal goals, and using role-play or demonstrations for home blood pressure monitoring.
- Follow-Up: Schedule regular check-ins or follow-up calls to review progress, address any concerns, and reinforce healthy habits.
Conclusion
Nursing teaching on hypertension is a cornerstone of chronic disease management. By providing comprehensive education and support, nurses can help patients understand their condition, make informed decisions, and adopt healthier lifestyles. This proactive approach not only improves individual outcomes but also contributes to the broader public health goal of reducing the prevalence and impact of hypertension worldwide.
This blog post emphasizes the nurse’s role in patient education, offering practical advice and strategies for engaging patients in managing their hypertension effectively.

